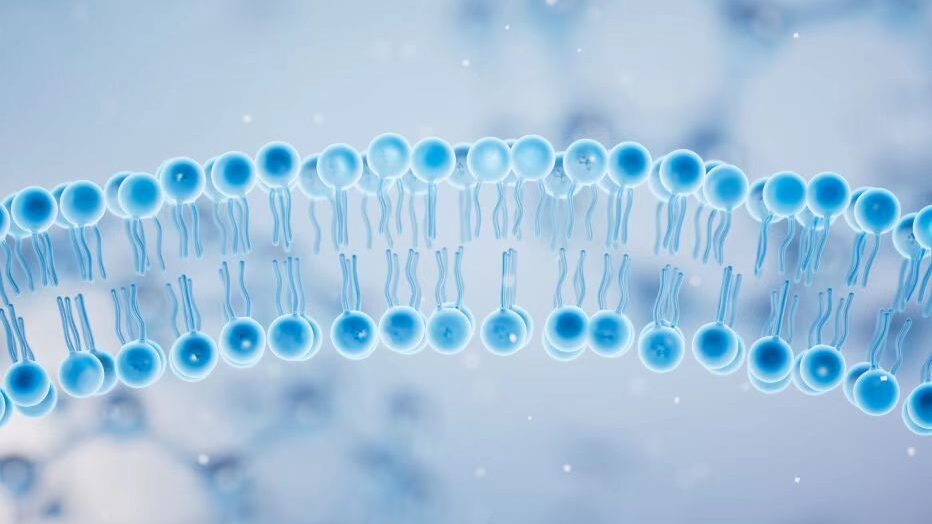
Phospholipids, also known as phospholipids, are lipids that contain phosphoric acid. Phospholipids are amphoteric molecules, one end is a hydrophilic nitrogen or phosphorus head, the other end is a hydrophobic long alkyl chain, so often with proteins, glycolipids, cholesterol and other molecules together to form a phospholipid bilayer, is an important part of biofilm.
It was isolated from egg yolk by Gobley in 1844, so it was named Lecithin (lecithin) in Greek. Lecithin is a very important nutrient, because of its unique nutritional value, known as the “third nutrient” alongside vitamins and proteins.
In pharmaceutics, natural phospholipids of pharmaceutical excipients are mainly soybean phospholipids from soybeans and egg yolk lecithin from eggs.

Egg yolk lecithin is a natural mixture of phospholipids extracted and refined from egg yolks and is amphiphilic (a hydrophilic nitrogen or phosphorus head at one end and a hydrophobic (lipophilic) long alkyl chain at the other end). According to the different types of skeleton alcohols, yolk lecithin is mainly divided into two categories: one is glycerol as the skeleton, called glycerophospholipids; The other group is sphingolipids, which are called sphingolipids.
The structural characteristics of glycerol lecithin are that the hydroxyl group on glycerol Sn-1 and Sn-2 is esterified by saturated or unsaturated fatty acids, and the hydroxyl group on Sn-3 is esterified by phosphoric acid, and phosphoric acid is connected to the base, depending on the different base groups, Glycerin lecithin main types including phosphatidylcholine (phosphatidylcholine, PC) and phosphatidyl ethanolamine (phosphatidylethanolamine, PE), phosphatidyl inositol (phosphatidylinositol, PI), phosphatidylserine (PS), phosphatidic acid (PA), and phosphatidylglycerol (PG). In addition to the above 6 types, the fatty acyl group of the glycerol Sn-1 position in the glycerophospholipid molecule is replaced by a long chain alcohol to form a vinyl ether, which is called plasmalogen glycerophospholipid. Phosphatidylphospholipids are replaced by phosphatidylphosphatidylphosphatidylphosphatidylphospholipids. Lysophosphatidylcholine is produced when glycerol lecithin is hydrolyzed by phospholipase and specific lipase. The structure and species of glycerophospholipids are shown in the figure below.
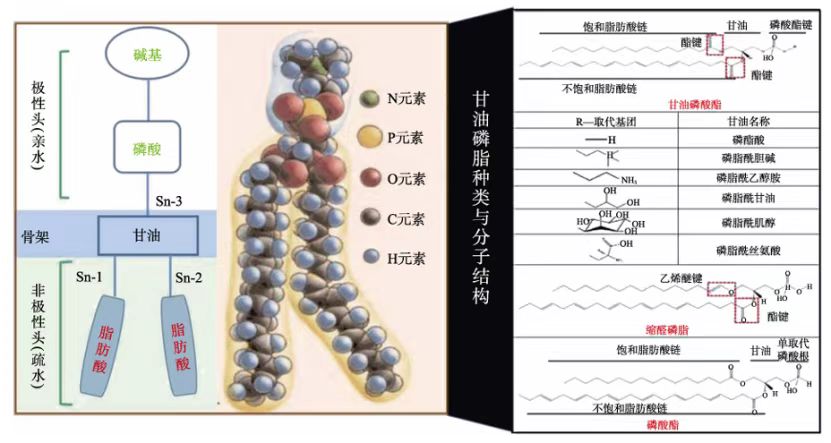
sphingolipid consists of sphingosine (sphingosine), fatty acids, phosphoric acid and nitrogenous bases. The fatty acyl group is connected with the amino group of neuroalcohol by amide bond, and the formed fatty acyl sphingosine is also called ceramide; The primary alcohol group of neuroalcohol is linked to phosphatidylcholine (or phosphatidylethanolamine) by a phosphate ester bond. The fatty acids found in sphingomyelin are palmitic acid, stearic acid, guppy tar acid, neuroleic acid and so on. The molecular structures of sphingosinol and sphingosphingomyelin are shown in the figure below.

physiological function
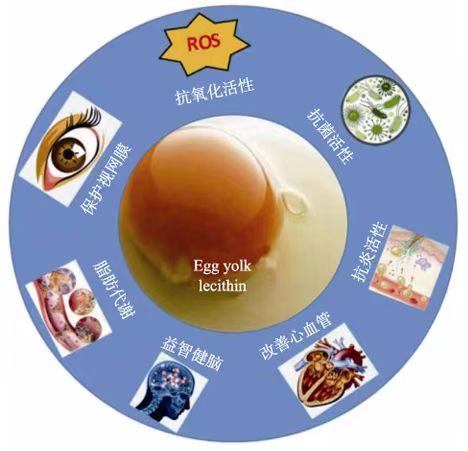

Egg yolk lecithin has many very important physiological functions, such as antioxidant activity, antibacterial activity, anti-inflammatory activity, improve fat metabolism, protect the retina, improve blood blood management, and brain health. The following is a brief introduction to the antioxidant, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory, neuroprotective and cardiovascular protection and other functional activities of yolk lecithin.
- Antioxidant activity
As early as 1992, it was reported that egg yolk lecithin has antioxidant activity, delaying the oxidative degradation of edible salmon oil, and it was also proved that the addition of N element can enhance the antioxidant activity of lecithin. Studies have shown that the degree of unsaturated fatty acids on the structure of egg yolk lecithin is positively correlated with its antioxidant activity. Phosphatidylcholine and phosphatidylethanolamine side chain hydroxylamine group have strong ability to inhibit lipid peroxidation, indicating that egg yolk lecithin side chain hydroxylamine acid is very important for lecithin antioxidant activity.
- Antimicrobial activity
The antibacterial activity of egg yolk lecithin refers to the formation of nanoscale liposomes or micelles of lecithin, the embedding of antibacterial active substances, and the combination of lecithin liposomes with microbial cells to release antibacterial active substances, so as to achieve the purpose of killing microorganisms or inhibiting the growth of microbial cells.
- anti-inflammatory activity
The mechanism of the anti-inflammatory activity of yolk lecithin is that lecithin uptake changes the metabolic pathway of inflammatory factors NF-κB and MAPK, and lecithin inhibits the up-regulation of inflammatory factors. The degree of unsaturated fatty acid chain of lecithin structure was positively correlated with the anti-inflammatory activity.
- Neuroprotective function
Alzheimer’s is a neurodegenerative disease that leaves the body with a loss of memory and a lack of cognition. Takeing in egg yolk lecithin can improve human memory and cognitive function, delay the occurrence of neurodegenerative diseases, especially the unsaturated fatty acid chain in yolk lecithin structure plays an indirect protective role. Some studies suggest that yolk lecithin can play a neuroprotective role by inhibiting the activity of acetylcholinesterase and down-regulating the concentration of oxidation products.
- Cardiovascular protective function
Epidemiological studies have shown that hypertension is a major factor causing cardiac diseases such as sudden death and coronary heart disease. Egg yolk lecithin lowers blood pressure by inhibiting angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE).
Application
In the 1960s, fat emulsion was developed and marketed by Fesenius Karbi based on egg yolk lecithin. Since then, natural phospholipids have become essential excipients for the development of fat emulsion , widely used in propofol emulsion injection, propofol medium/long chain fat emulsion injection,flurbiprofen axetil injection, Alprostadil fat emulsiom injection, medium and long chain fat emulsion injection and other drugs.
In addition,egg yolk lecithin can be used to make liposomes, and can also be used as emulsifier in fat injection, and has certain efficacy in prevention of and cerebrovascular diseases and tumor. In the food industry, egg yolk lecithin has also been widely used in all kinds of health food and infant food to meet the needs of the body for lecithin at different growth period.
01 Propofol emulsion injection
As a short-acting intravenous anesthetic, propofol is one of the commonly used sedative drugs for anesthesia induction in clinical practice, and egg yolk lecithin as a emulsifier in oil-in-water (O/W) emulsion.

02 Alprostadil injection
Alprostadil is mainly used for myocardial infarction, thromboangiitis, occlusive arteriosclerosis and other diseases.

03 Flurbiprofen axetil injection
Flurbiprofen ester is used for analgesia after surgery and various cancers, with the advantage that it has no central inhibitory effect and does not affect the recovery of patients under anesthesia, and can be used immediately after surgery.
04 Medium/Long chain Fat Emulsion Injection (C6 ~ 24)
Medium/long chain fat emulsion injection (C6 to 24) solution is used for patients who need to receive parenteral nutrition and/or essential fatty acid deficiency.


