Xanthan gum can be used in pharmaceutical industry because of its safety, emulsification, thickening, stability, film formation and gelling. The United States Food and Drug Administration approved xanthan gum as a food additive in 1969, and the European Union approved it as a food stabilizer and emulsifier in 1980. In the field of medicine, xanthan gum was collected by the United States Pharmacopoeia/National Formulary in 1975, and by the Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China as a pharmaceutical excipient in 2010.
Product introduction

product feature
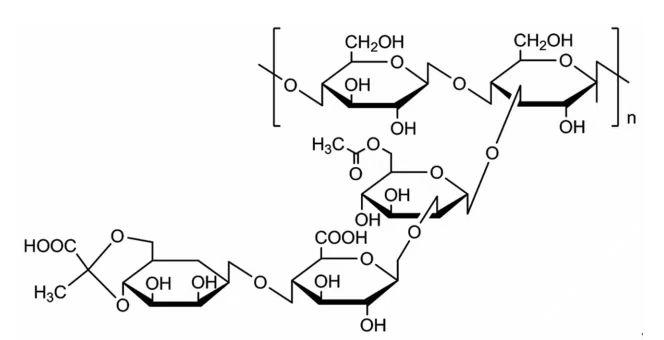
1. Water solubility
Xanthan gum dissolves quickly in water and has good water solubility. Especially in cold water can also be dissolved, can save complicated processing process, easy to use.
2. Stability
In the secondary structure of xanthan gum, the side chain is reversed by winding the main chain, so that the main chain is protected and not easily degraded, so that it has the characteristics of high temperature resistance, acid and alkali resistance, salt resistance and enzymatic hydrolysis resistance.
3. Rheology
Xanthan gum solution is a typical pseudoplastic fluid. Under the action of shear force, the viscosity decreases sharply, and the higher the shear speed, the greater the viscosity decreases. When the shear effect disappears, the viscosity immediately recovers to the maximum.
4. Thickening
Because the tertiary structure of xanthan gum is a network structure, it has good water flow control properties, so it has good thickening property, especially at low mass concentration with high viscosity. 0.3g/L xanthan gum solution has a viscosity of 90mPa▪s. The viscosity of xanthan gum solution is about 100 times that of gelatin with the same mass concentration.
5.suspension and emulsification
Xanthan gum has good suspension effect on insoluble solids and oil droplets. Xanthan colloidal molecules can form superbinding ribbon helical copolymers, forming a fragile glue-like network structure, so it can support the form of solid particles, droplets and bubbles, showing strong emulsifying stability and high suspension capacity.
6. Security
Xanthan gum is a kind of safe biological polysaccharide. Short-term feeding experiments show that xanthan gum is non-toxic to rats and dogs, has no growth inhibiting effect, and has no irritation to eyes and skin. Xanthan gum was approved by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1969, was collected by the United States National Formulary (NF) in 1975, was approved by the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) and the World Health Organization (WHO) in 1983 as a food additive, and was collected by the Chinese Pharmacopoeia as a pharmaceutical excipient in 2010.
product application
Solid preparation
Xanthan gum is used in solid preparation as disintegrating agent, binder, sustained-release agent, controlled release agent, etc. The good adhesion of xanthan gum makes it suitable for both water-soluble drugs and inwater-soluble drugs, such as antipyretic and analgesic drugs, anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamins, etc., to prepare sustained-release tablets with different hardness, dissolution rate and viscosity with various excipients. When used as a binder to make a film, various accessories can be added to adjust the hardness, prevent the film from being hard, and cracks appear during the pressing process and storage; Xanthan gum is an important component of microencapsulated drug capsules, which can control drug release. Xanthan gum can also be used as an excipient for chewable tablets or sucking tablets; Xanthan gum can also be used as a substrate for other oral dosage forms.

Ingredients: Amberlite® Resin, Gelatin, Mannitol, Glycine, dimethicone, Carbomer, Sodium Hydroxide, Aspartame, Red iron oxide, peppermint Oil, Xanthan gum
Liquid and semi-solid preparations
Xanthan gum is used as thickening agent, suspension agent, emulsifier and stabilizer. The high viscosity of xanthan gum makes the topical preparation easier to be coated, and the drug is not easy to fall off from the skin after volatilization of water, which improves the bioavailability and drug comfort.

Ingredients: Pre-gummed starch, Sodium benzoate, Xanthan gum, glycerin, sucrose, anhydrous citric acid, Tween 80, food coloring, food flavor, pure water
Ingredients: Sodium benzoate, Sorbitol, Monosodium anhydrous citrate, Xanthan gum, titanium dioxide, Saccharin sodium, tutti-frutti flavoring agent
Ophthalmic preparation
Xanthan gum as an eye drop additive can extend the contact time between the drug and the application site. Due to its pseudo-plastic fluid nature, the shear force generated during blinking can rapidly reduce its viscosity without causing discomfort to the eyes. The mixture of xanthan gum, chondroitin sulfate and sodium hyaluronate can protect corneal epithelial cells and accelerate cell regeneration. The ophthalmic gel prepared with xanthan gum as the gel matrix is uniform, stable and has good gel strength. It has good bioadhesive effect on the corneal surface, and can significantly prolong the drug retention time, improve the therapeutic effect and delay the drug release.
Product recommendation
Pharmacopoeia: USP/NF, EP, JP, Ch.P
CDE Registration Number Status: “A”

