Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an acute respiratory infectious disease caused by the influenza virus. Unlike the common cold, it has a rapid onset and often presents with more severe symptoms, including high fever, headache, fatigue, muscle aches, and more. It can significantly impact a patient’s quality of life and may even lead to serious complications such as pneumonia or myocarditis, posing a threat to life and health. During flu season, choosing the right medication for treatment is crucial, as it not only alleviates symptoms but also shortens the course of the illness and reduces the risk of complications.
Medications for influenza fall into two main categories: antiviral drugs and symptomatic treatment medications.
Anti-Influenza Medication
Oseltamivir Phosphate for Oral Suspension
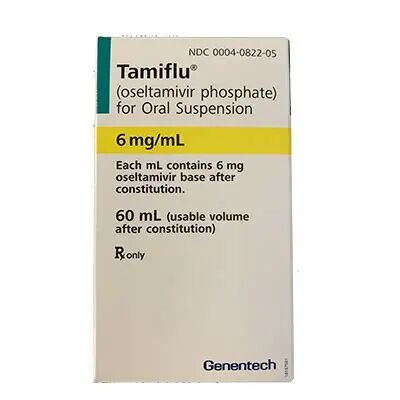
Indications: For the treatment of influenza A and B in adults and pediatric patients 2 weeks of age and older. For the prophylaxis of influenza A and B in patients 1 year of age and older.
Inactive Ingredients: Sodium benzoate, monosodium citrate anhydrous, xanthan gum, titanium dioxide, sorbitol, sodium saccharin, flavoring.
2 Aspirin and Vitamin C Effervescent Tablets
Indications: For the relief of fever (including fever due to colds), headache, sore throat, toothache, and other pains.
Inactive Ingredients: monoodium citrate anhydrous, sodium bicarbonate, citric acid anhydrous, sodium carbonate anhydrous.

3 Ibuprofen Suspension
Indications: For the reduction of fever in children with common cold or influenza.
Inactive Ingredients: Pregelatinized starch, xanthan gum, glycerol, sucrose, citric acid anhydrous, sodium benzoate, polysorbate 80, food color, food flavor, purified water.
Monosodium Citrate Anhydrous
Monosodium Citrate Anhydrous
Description:A white powder or crystalline granular substance.
Characteristics:Slightly acidic taste; readily soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol; low hygroscopicity, low moisture content; good compressibility; nontoxic, nonallergenic, and nonGMO.
Sodium citrate anhydrous is a monosodium salt of citric acid. It is produced by partially neutralizing citric acid with a highpurity sodium source, followed by crystallization or spraydrying.
The properties of this partially neutralized salt lie between those of citric acid and trisodium citrate (neutral or weakly alkaline). Therefore, sodium citrate anhydrous is recommended when a buffering effect is desired or when the buffering effect of citric acid alone is considered too strong for the formulation.
Compared with citric acid, sodium citrate anhydrous exhibits lower hygroscopicity, reduced tendency to clump, and serves as a key excipient in formulations such as dry suspensions, fastdissolving preparations, or tablets.

Xanthan Gum
Xanthan Gum
Description: Light yellow to white freeflowing powder with a slight characteristic odor.
Characteristics: Easily soluble in cold or hot water, yielding a neutral solution; resistant to freezing and thawing; insoluble in ethanol. Upon contact with water, it disperses and emulsifies to form a stable, hydrophilic viscous gel.
Xanthan gum is a classic highly pseudoplastic fluid. Under shear stress, its viscosity drops sharply—the higher the shear rate, the greater the viscosity reduction.Once shear is removed, viscosity recovers almost instantly. It exhibits stable physicochemical properties, including heat resistance, tolerance to acids and alkalis, and resistance to enzymatic degradation.It is compatible with all common excipients, active ingredients, and packaging materials. Effective at low concentrations, it offers high performance and helps reduce costs and dosageform specification.
Due to its safety, suspending ability, thickening effect, stability, filmforming property, and gelling capability, xanthan gum is widely used in solid, semisolid, liquid, and ophthalmic preparations.


