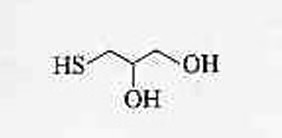
Product Name: Monothioglycerol
Description: Colorless or pale yellow, viscous, hygroscopic liquid with a slight sulfide odor.
Use: Antioxidant
Chemical Name: 3-Mercapto-1,2-propanediol, which is a derivative of glycerol where one hydroxyl group is replaced by a mercapto (-SH) group. This structural feature gives it unique chemical properties, specifically:
Strong Reducing Property: The mercapto (-SH) group is the core functional group through which Monothioglycerol exerts its antioxidant effect. It actively reacts with oxidizing substances such as oxygen and free radicals, thereby inhibiting the oxidative degradation of drug components.
Excellent Water Solubility: Retains the hydrophilic groups of glycerol, making it fully soluble in aqueous media, suitable for aqueous formulation systems like injections and oral solutions.
Good Biocompatibility: Pharmaceutical-grade Monothioglycerol complies with major pharmacopoeial standards such as USP/EP/JP, exhibits very low toxicity, and has reliable safety within the specified dosage range.
Compared to common antioxidants like Vitamin C and sodium sulfite, Monothioglycerol offers advantages such as high antioxidant efficiency, strong inherent stability, and a lower tendency to interact with other components in the formulation. It is particularly suitable for pH-sensitive or metal ion-containing formulation systems.
Application

Formulation Name: Vitamin B1 Injection
Inactive Ingredients: Chlorobutanol anhydrous, Monothioglycerol, Water for Injection, Sodium Hydroxide

Formulation Name: Bendamustine Hydrochloride Injection
Inactive Ingredients: Propylene Glycol, Monothioglycerol, Polyethylene Glycol 400, Sodium Hydroxide, Water for Injection
Precautions
Dosage Control: The typical usage range is 0.05%–0.5%. Excessive use may lead to a characteristic mercaptan odor in the formulation or increase the risk of local irritation.
Storage Conditions: Due to its inherent reducing property, thioglycerol should be stored sealed, protected from light, in a cool place, and kept away from strong oxidizing agents.
Metal Ion Chelation: If the formulation contains metal ions such as iron or copper, co-use with chelating agents like EDTA is recommended, as metal ions may catalyze oxidation reactions and affect the antioxidant efficiency of thioglycerol.
pH Compatibility: Antioxidant effect is optimal in neutral to weakly alkaline environments. Its efficacy may be reduced under acidic conditions, so the dosage should be adjusted rationally based on the formulation’s pH.

