Polyethylene glycol series
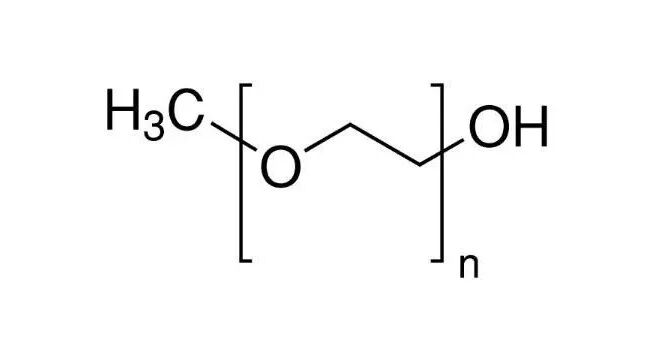
glycol (PEG), a petroleum-derived polyether compound, exists as a liquid or solid depending on its molecular weight. It is widely used in liquid pharmaceutical formulations (e.g., oral liquids, injections), semisolid formulations (e.g., ointments, suppositories) and solid formulations (e.g., tablet coating). As a stable hydrophilic compound, PEG can serve as an ointment base (with consistency controlled by adjusting the ratio of solid and liquid grades), a suppository base (offering advantages such as adjustable melting point and excellent physical stability over fatty bases), as well as a tablet binder and film coating material (with both plasticizing and lubricating properties). Its characteristics vary significantly with changes in molecular weight.
Polyethylene glycol is composed of repeating ethylene glycol units and has a wide molecular weight distribution, ranging from 200 Daltons (PEG 200) to not less than 20,000 Daltons (PEG 20000). The numerical suffix denotes its average molecular weight (e.g., PEG 400 is approximately 400 Daltons). The molecular weight of PEG increases with the rise in its degree of polymerization (n); for instance, n is about 8-9 for PEG 400 and around 136 for PEG 6000.PEG with a molecular weight of less than 1000 Daltons appears as a colorless, transparent, viscous oily liquid at room temperature (e.g., PEG 400 is commonly used as a solvent). When the molecular weight ranges from 1000 to 10,000 Daltons, it is a semisolid unguent with a waxy and flexible texture at room temperature (e.g., PEG 1500 is applied as an ointment base). For PEG with a molecular weight exceeding 10,000 Daltons, it exists as a white solid powder or flake that is easily pulverized at room temperature (e.g., PEG 6000 is used as a suppository base).
Core Advantages of PEG: High biocompatibility (no immunogenicity with an extremely low incidence of allergic reactions), high chemical stability (resistant to hydrolysis and oxidation with good compatibility with most active pharmaceutical ingredients), excellent solvency (capable of dissolving both water-soluble and fat-soluble drugs), and low toxicological risk.
Polyethylene glycol (PEG) acts as a solvent with three key functions:
(1) Enhancing the solubility of poorly soluble drugs.
(2) Improving the stability of drugs susceptible to degradation in aqueous environments
(3) For injections using PEG as the solvent, the drug can form a local drug reservoir after injection, thereby prolonging the duration of drug action.
01. Polyethylene glycol 300 (for injection use)
Polyethylene glycol 300 (for injection use) is an injection aid material. It is mainly used as a solvent and a solubilizer to enhance the solubility of poorly soluble drugs and improve the stability of the formulation.
PEG300 can effectively increase the solubility of poorly soluble drugs, has good water solubility and low viscosity properties, can be miscible with common injection solvents such as water and ethanol in any proportion, has stable chemical properties, low endotoxin content and good biocompatibility.

Methocarbamol Injection
Inactive Ingredients: Polyethylene Glycol 300, Water for Injection, Hydrochloric Acid and/or Sodium Hydroxide
02.Polyethylene Glycol 400 (for injection use)
PEG 400 has a molecular weight of approximately 380–420 Daltons, presenting as a colorless and transparent liquid with a moderate viscosity (about 80–110 mPa·s at 25 °C). It has similar solubility to PEG 300 but slightly better stability and low volatility.
PEG 400 combines low viscosity with high stability, featuring broader compatibility with drugs and other excipients, and can balance the solubilization effect with the long-term stability of the preparation.
Preparation Name: Methocarbamol Injection
Inactive Ingredients: Ethanol 96%, Polyethylene Glycol 400, Sodium Citrate, Anhydrous Citric Acid, Water for Injection
reparation Name : Busulfan Injection
Inactive Ingredients: Dimethylacetamide, Polyethylene Glycol 400
Polyethylene Glycol 3350 (for injection use)
The molecular weight of PEG3350 is approximately 3000-3700. It is a white powder. At 25℃, its solubility in water is about 75g/100mL. The viscosity of the aqueous solution is relatively high (at 25℃, the viscosity of a 10% solution is approximately 150-200 mPa·s). It has good ball-forming properties and biodegradability.
PEG3350 is of high purity and is not metabolized in the body. It is mainly excreted through the kidneys in its original form.
As a carrier, it can control the release rate of drugs and prolong the efficacy.
Preparation Name: Compound Betamethasone Injection
Inactive Ingredients: Disodium Hydrogen Phosphate Dihydrate, Sodium Chloride, Disodium Edetate, Polysorbate 80, Benzyl Alcohol, Methyl Parahydroxybenzoate, Propyl Parahydroxybenzoate, Sodium Carboxymethyl Cellulose, Polyethylene Glycol 3350, Water for Injection
Preparation Name: Medroxyprogesterone Acetate Injection
Inactive Ingredients: Polyethylene Glycol 3350, Polysorbate 80, Sodium Chloride, Methyl Parahydroxybenzoate, Propyl Parahydroxybenzoate, Water for Injection, Sodium Hydroxide and/or Hydrochloric Acid

